Deploy Chaos Mesh on KubeSphere

Chaos Mesh is a cloud-native Chaos Engineering platform that orchestrates chaos in Kubernetes environments. With Chaos Mesh, you can test your system's resilience and robustness on Kubernetes by injecting various types of faults into Pods, network, file system, and even the kernel.
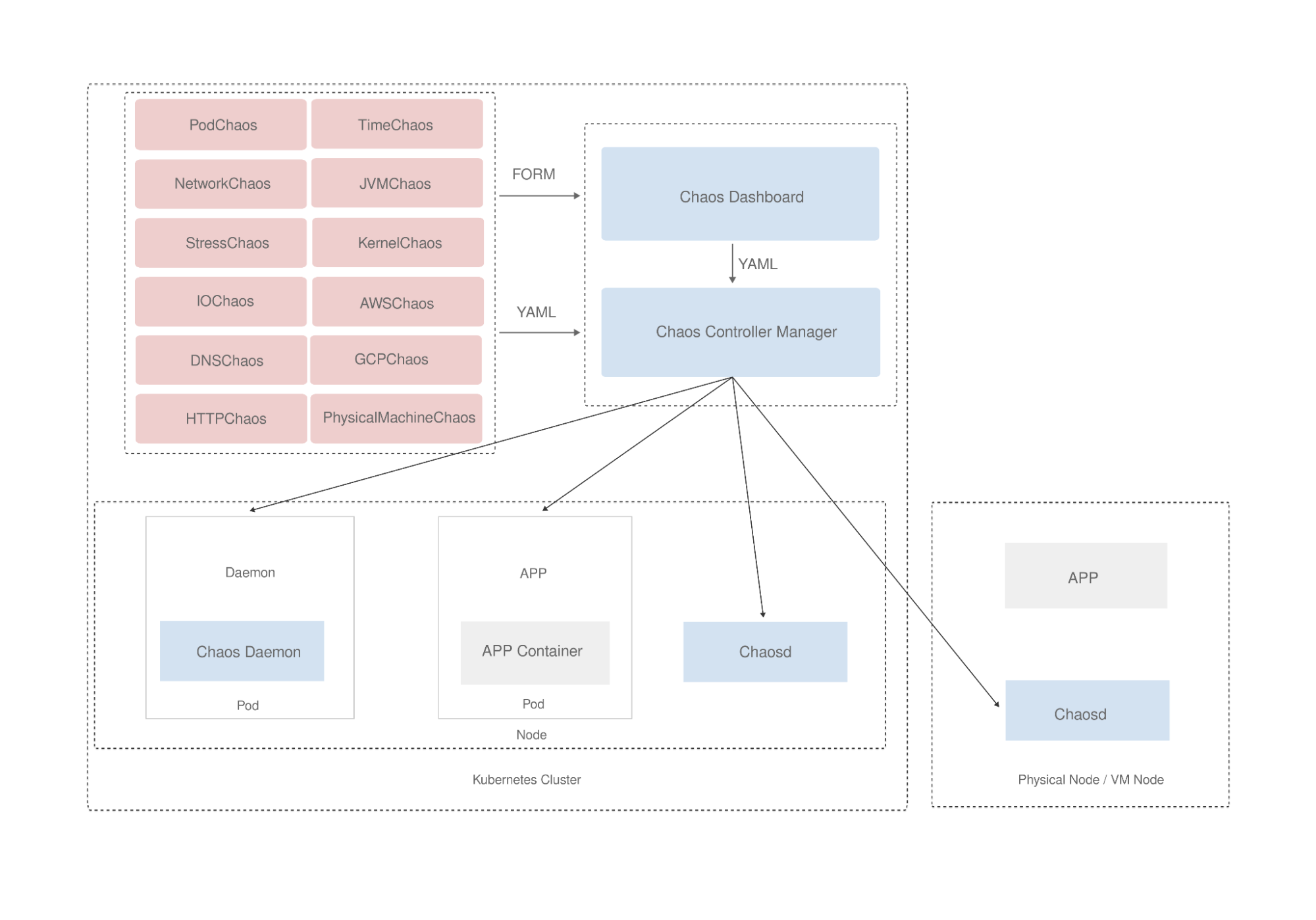
What’s KubeSphere
KubeSphere is a distributed operating system for cloud-native application management, using Kubernetes as its kernel. It provides a plug-and-play architecture, allowing third-party applications to be seamlessly integrated into its ecosystem.
KubeSphere 3.2.0 adds the feature of dynamically loading community-developed Helm charts into the KubeSphere App Store. Thanks to this new feature, Chaos Mesh is now available on KubeSphere. In this tutorial, you will learn how to deploy Chaos Mesh on KubeSphere to conduct chaos experiments.
Enable App Store on KubeSphere
-
Make sure you have installed and enabled the KubeSphere App Store.
-
You need to create a workspace, a project, and a user account (project-regular) for this tutorial. The account needs to be a platform regular user and to be invited as the project operator with the operator role. For more information, see Create Workspaces, Projects, Users and Roles.
Chaos experiments with Chaos Mesh
Step 1: Deploy Chaos Mesh
-
Login KubeSphere as
project-regular, search for chaos-mesh in the App Store, and click on the search result to enter the app.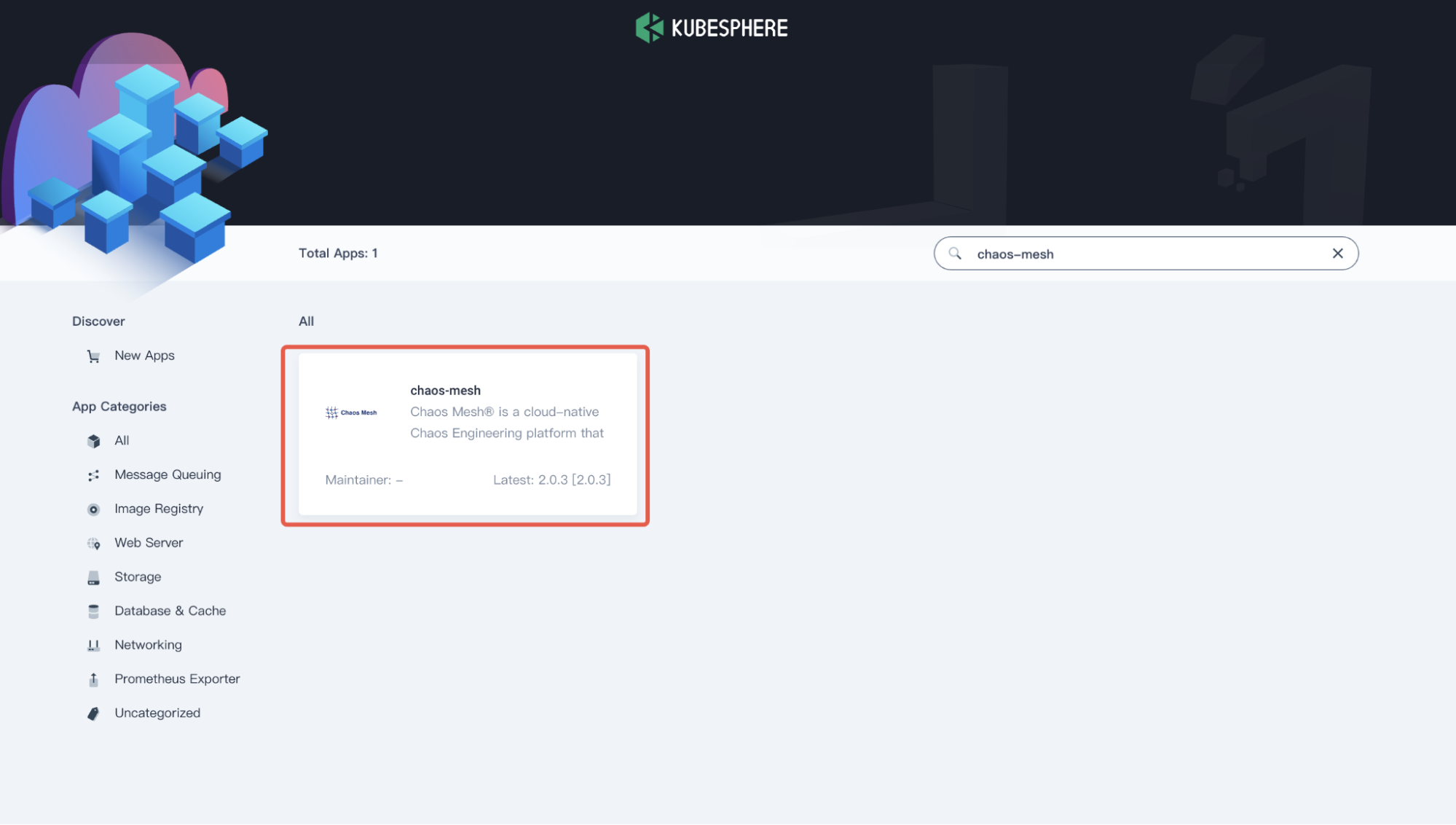
Chaos Mesh app -
In the App Information page, click Install on the upper right corner.
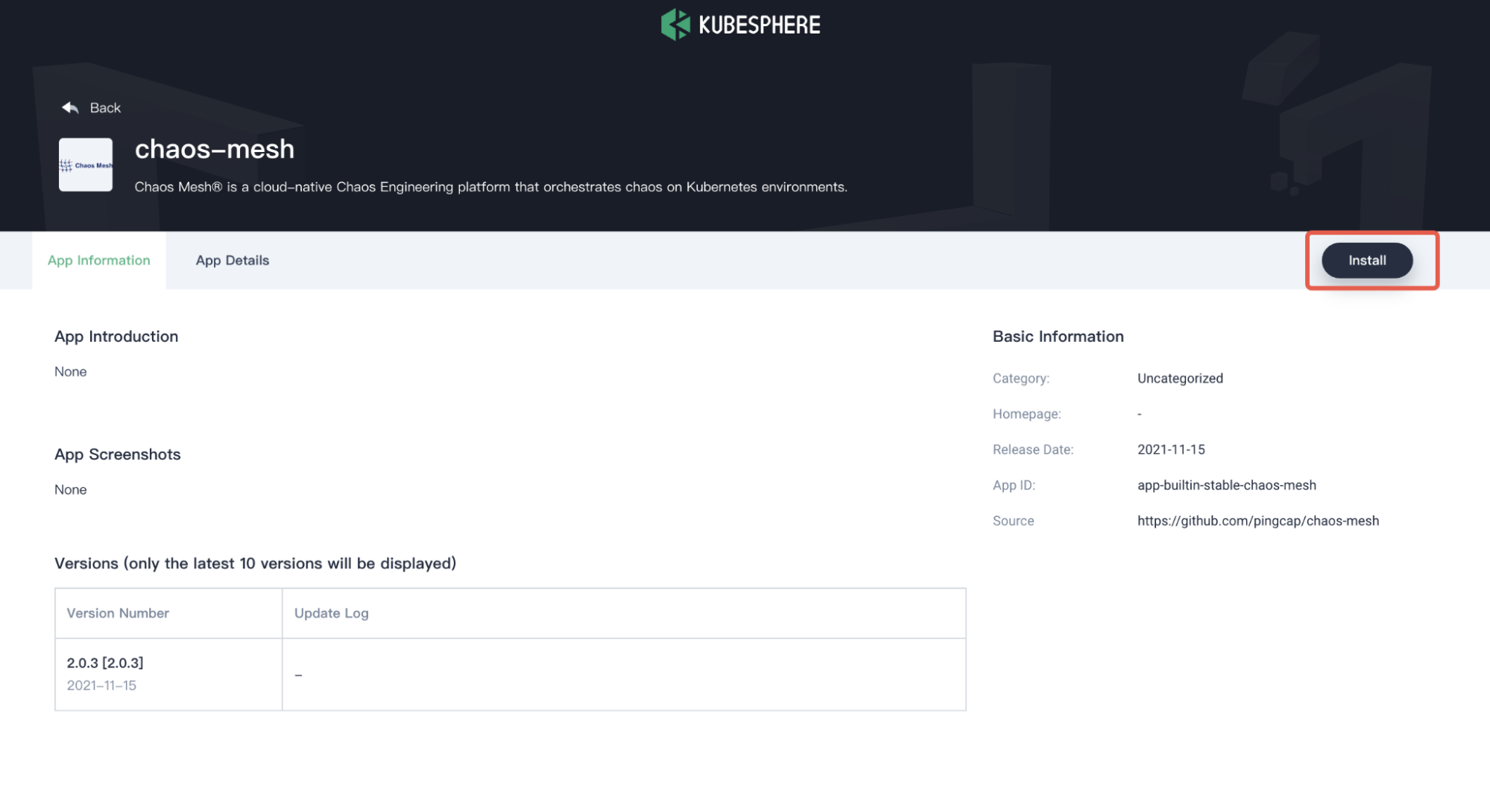
Install Chaos Mesh -
In the App Settings page, set the application Name, Location (as your Namespace), and App Version, and then click Next on the upper right corner.
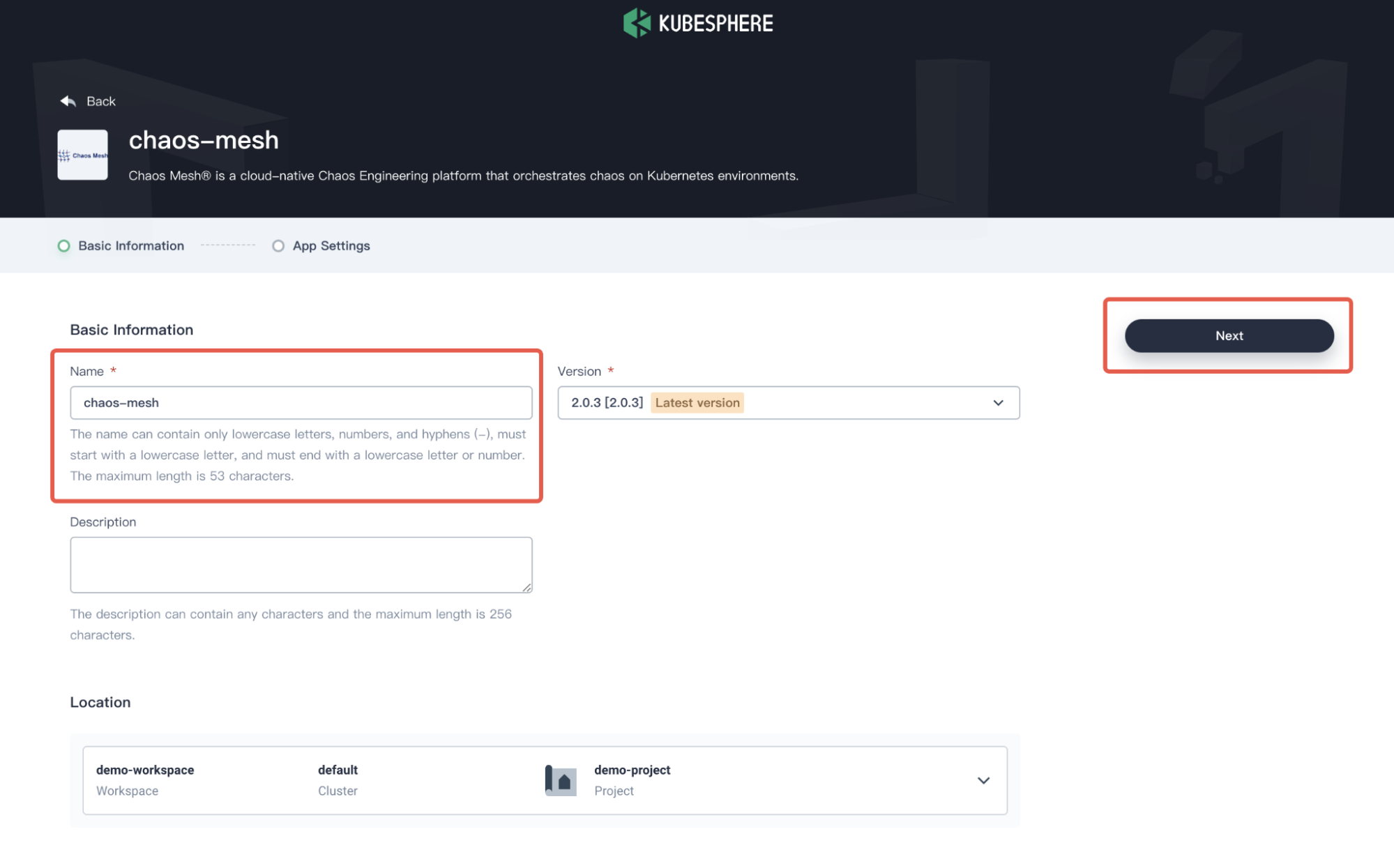
Chaos Mesh basic information -
Configure the
values.yamlfile as needed, or click Install to use the default configuration.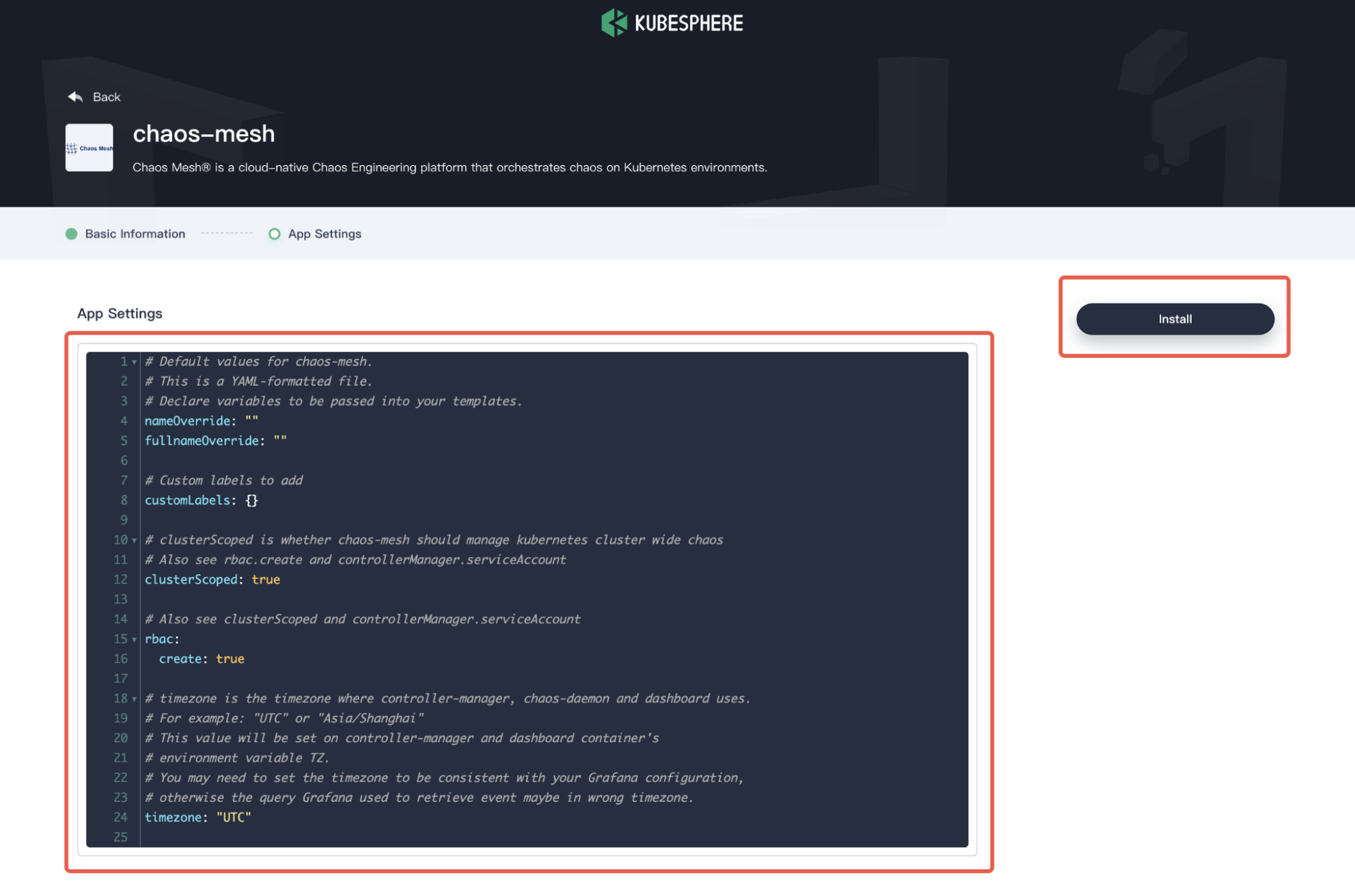
Chaos Mesh configurations -
Wait for the deployment to be finished. Upon completion, Chaos Mesh will be shown as Running in KubeSphere.
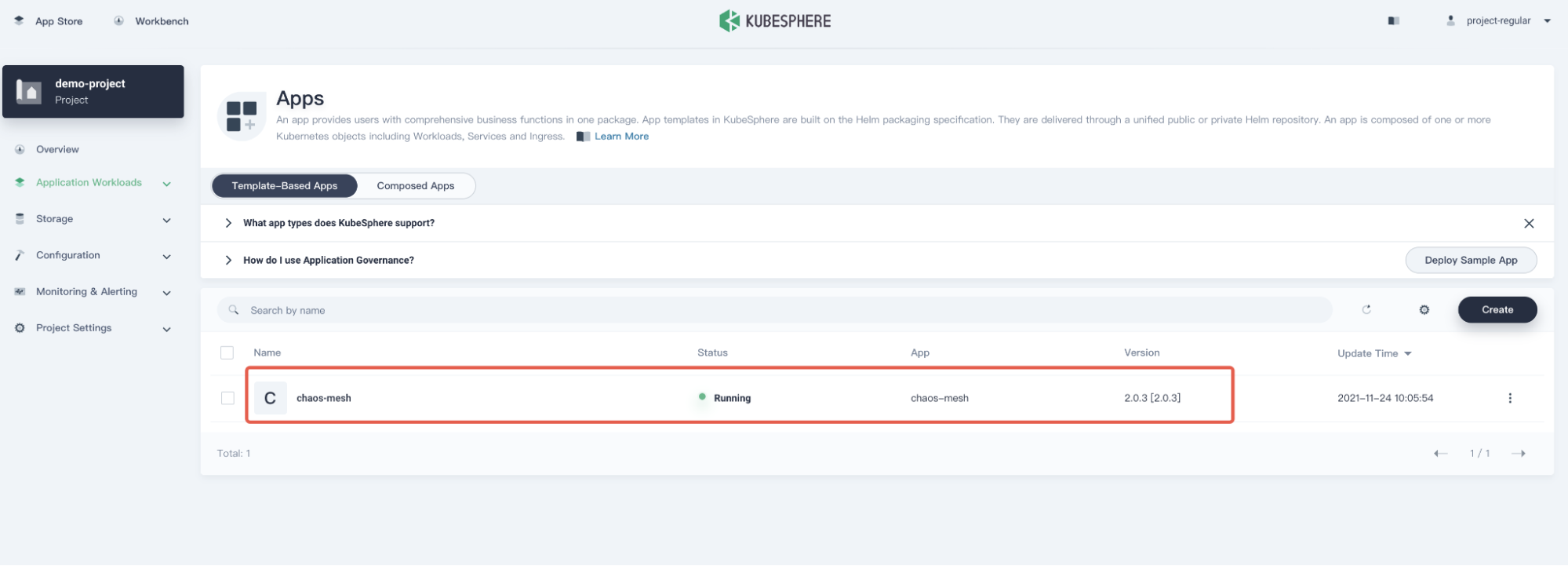
Chaos Mesh deployed
Step 2: Visit Chaos Dashboard
-
In the Resource Status page, copy the **NodePort **of
chaos-dashboard.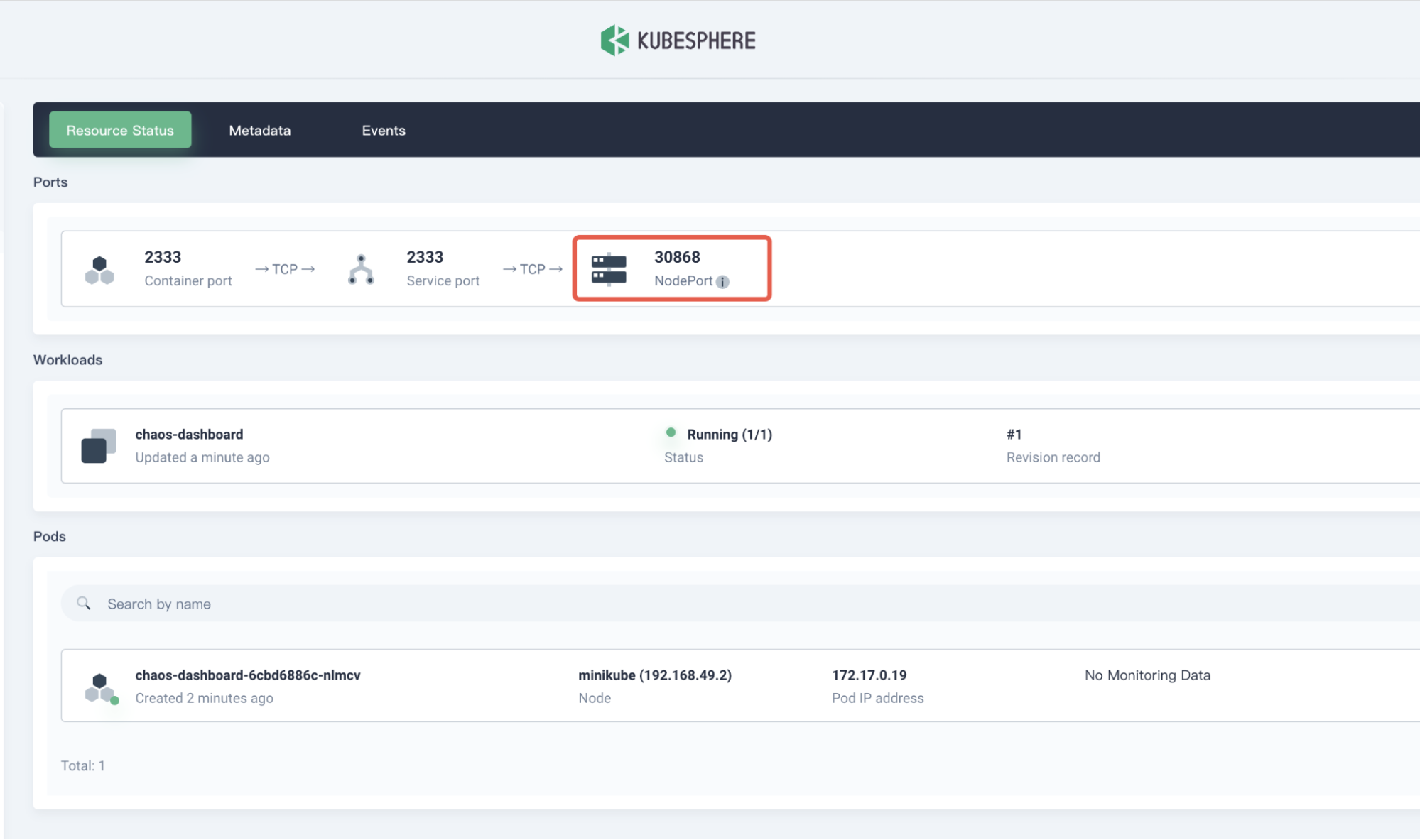
Chaos Mesh NodePort -
Access the Chaos Dashboard by entering
${NodeIP}:${NODEPORT}in your browser. Refer to Manage User Permissions to generate a Token and log into Chaos Dashboard.
Login to Chaos Dashboard
Step 3: Create a chaos experiment
Before creating a chaos experiment, you should identify and deploy your experiment target, for example, to test how an application works under network latency. Here, we use a demo application web-show as the target application to be tested, and the test goal is to observe the system network latency. You can deploy a demo application web-show with the following command: web-show.
curl -sSL https://mirrors.chaos-mesh.org/latest/web-show/deploy.sh | bash
Note: The network latency of the Pod can be observed directly from the web-show application pad to the kube-system pod.
-
From your web browser, visit
${NodeIP}:8081to access the Web Show application.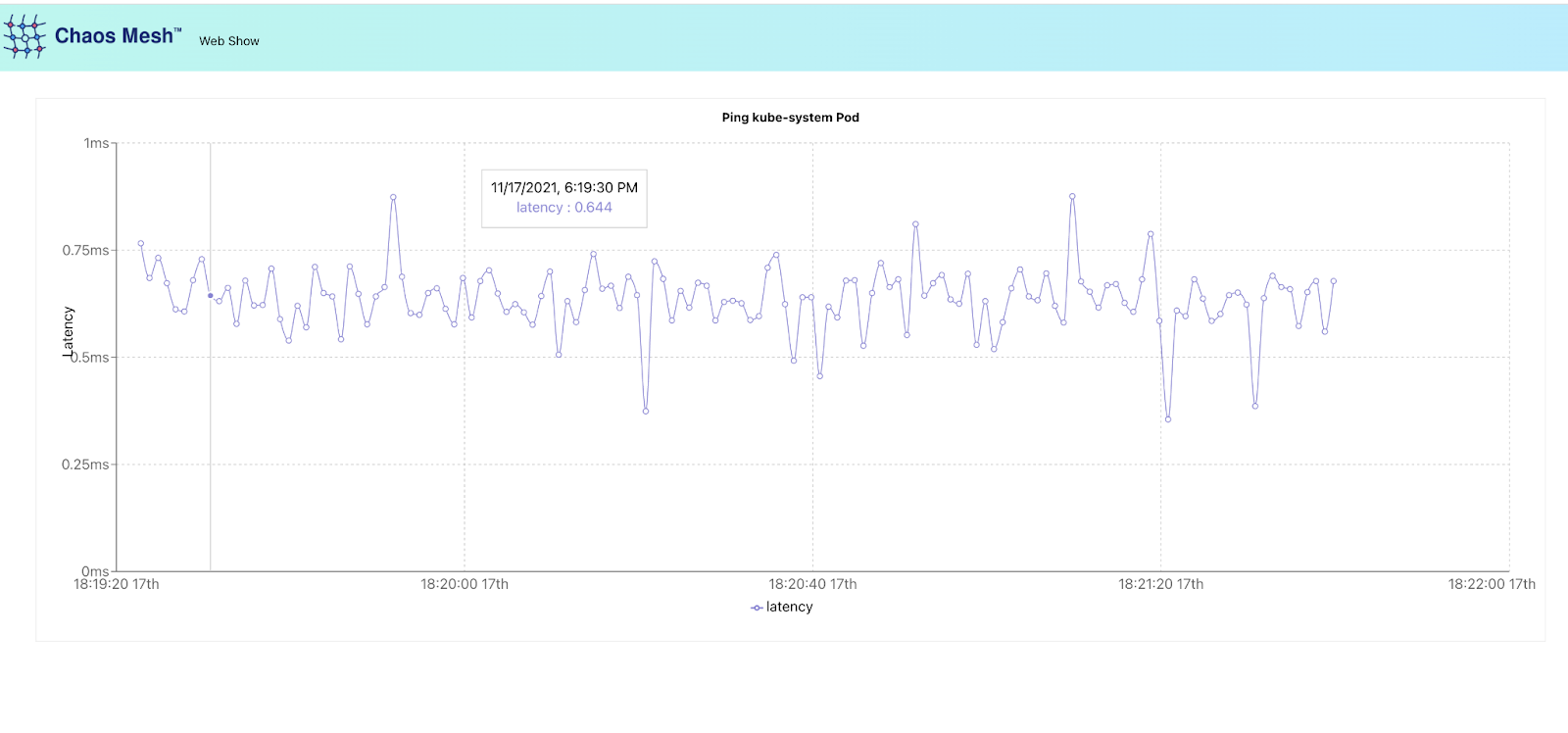
Chaos Mesh web show app -
Log in to Chaos Dashboard to create a chaos experiment. To observe the effect of network latency on the application, we set the **Target **as "Network Attack" to simulate a network delay scenario.
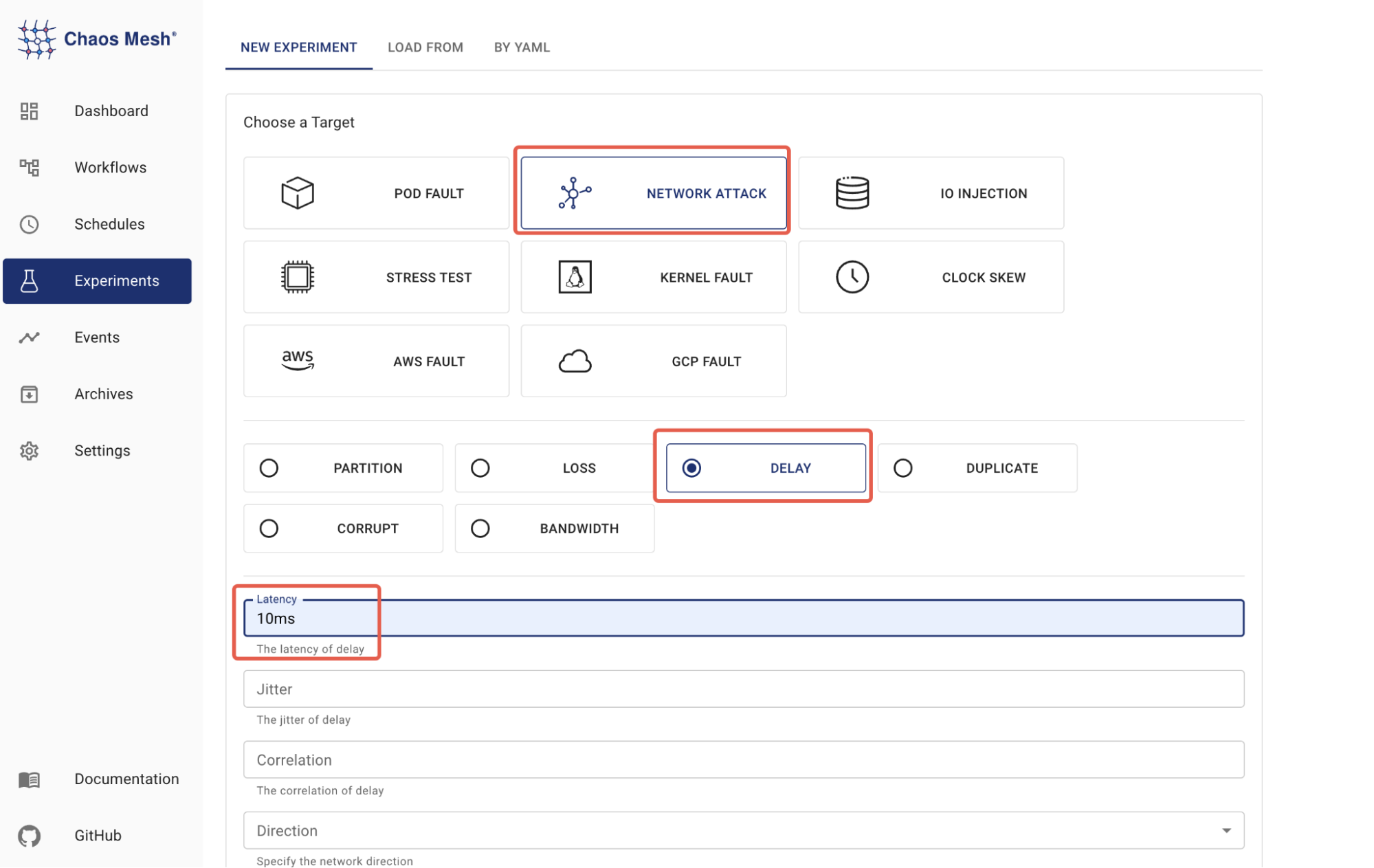
Chaos Dashboard The Scope of the experiment is set to
app: web-show.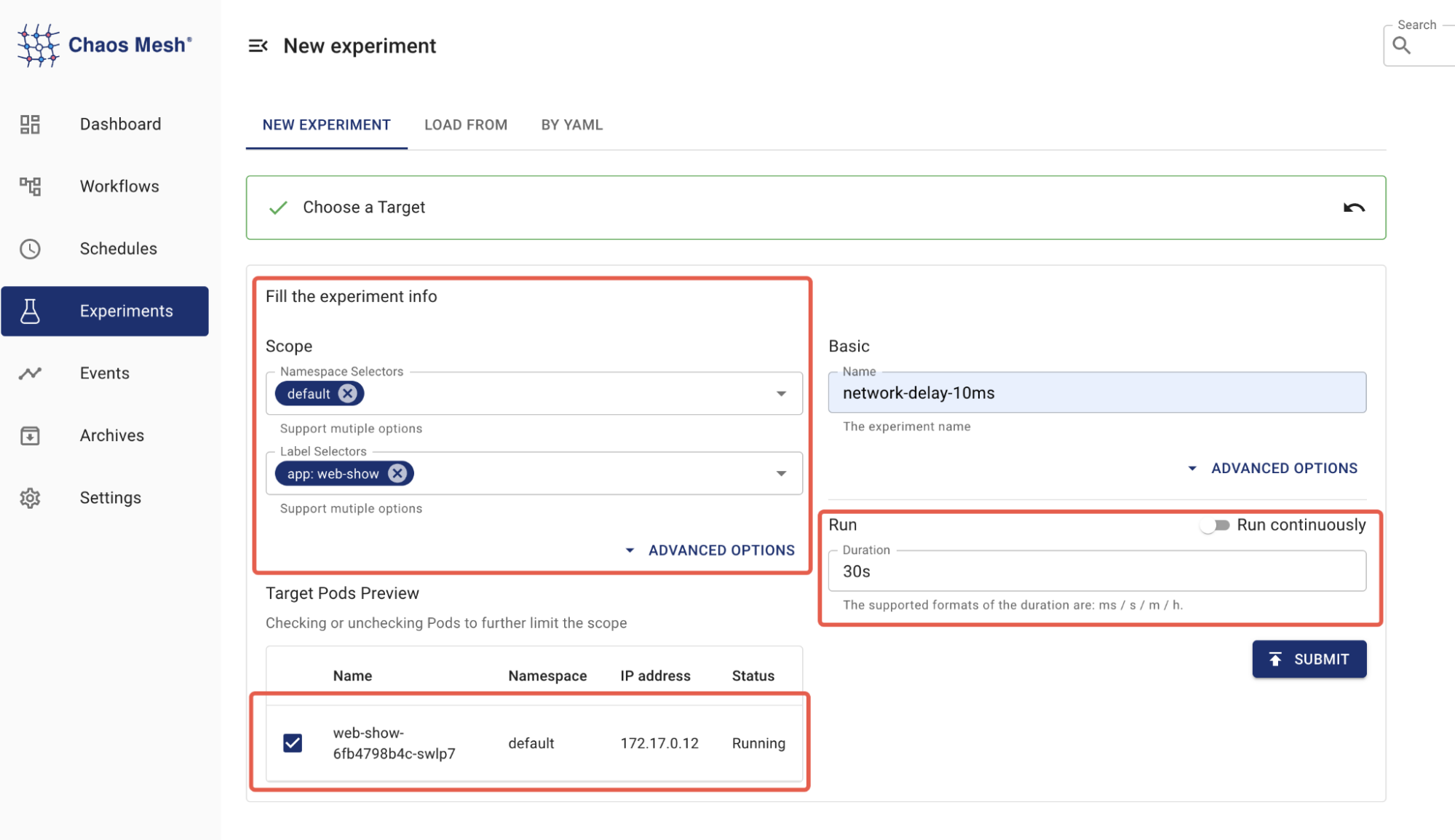
Chaos Experiment scope -
Start the chaos experiment by submitting it.
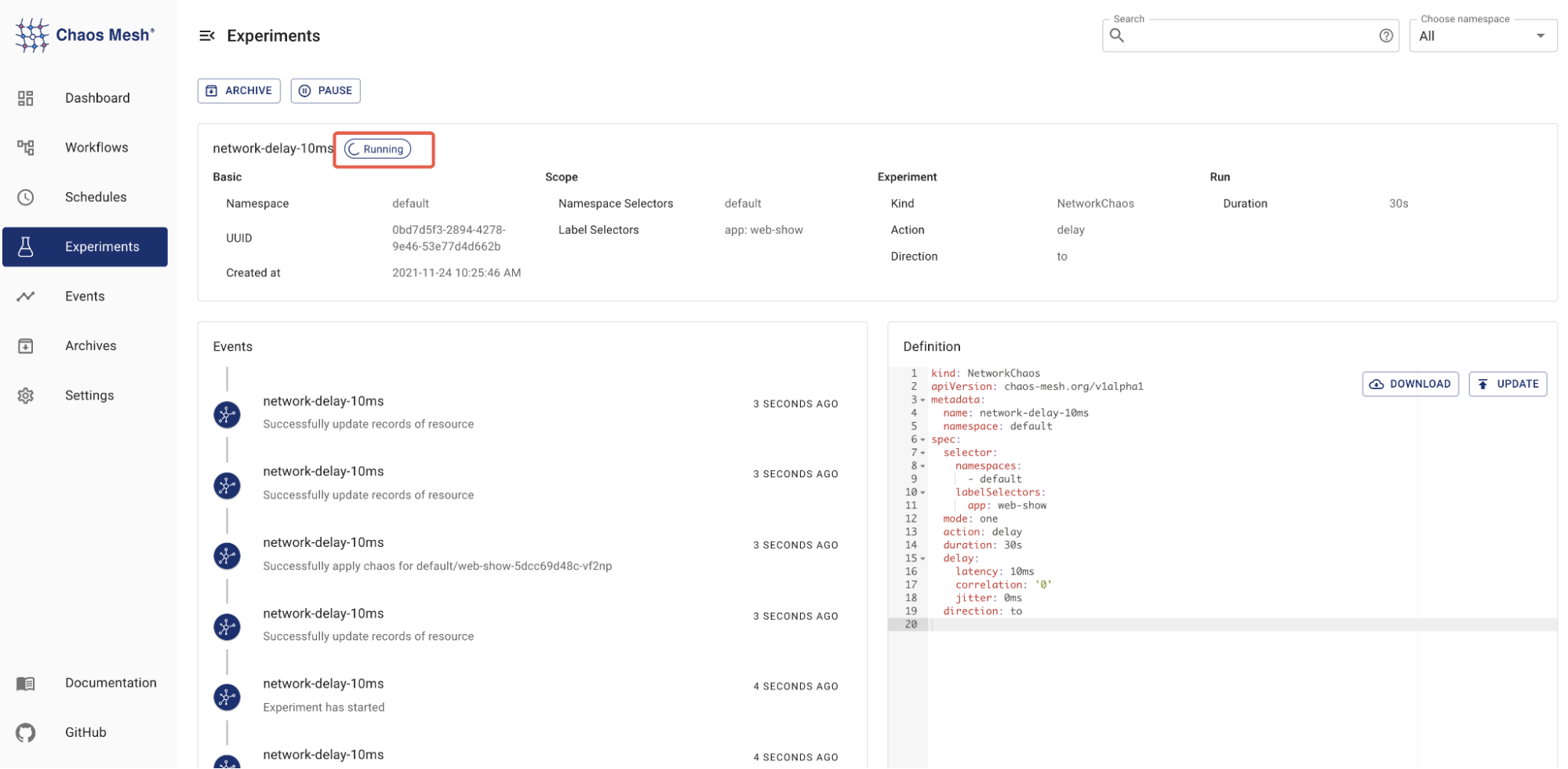
Submit Chaos Experiment
Now, you should be able to visit Web Show to observe experiment results:
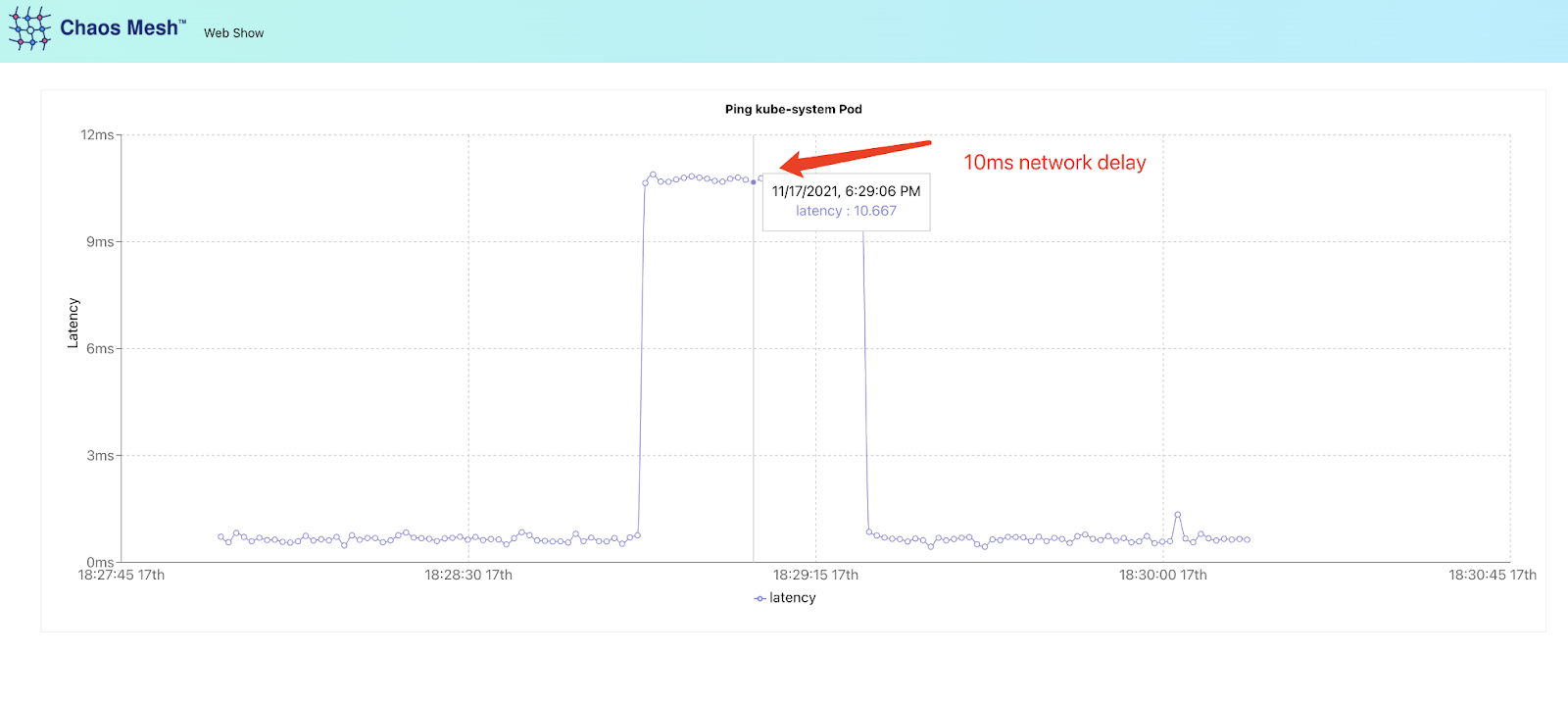
To summarize
KubeSphere makes cloud-native application deployments and maintenance easy. Thanks to the App Store, users can easily deploy Chaos Mesh on KubeSphere with just a few clicks, enabling you to quickly start your own chaos experiments.
To learn more about Chaos Mesh, refer to the Chaos Mesh docs or join the community Slack (CNCF/#project-chaos-mesh).