Manage User Permissions
This document describes how to manage user permissions in Chaos Mesh, including creating user accounts with different roles, binding permissions to user accounts, managing tokens, and enabling or disabling permission authentication.
Chaos Mesh uses RBAC Authorization to manage user permissions. To create, view and manage chaos experiments, users must have the appropriate permissions in the apiGroups of chaos-mesh.org to refer the resources of chaos experiments.
Chaos Mesh allows you to disable permission authentication, see Enable or disable permission authentication to learn how to disable it.
Note that we do not recommend disabling permission authentication in production environments.
Create user accounts and bind permissions
You can use the Chaos Dashboard to help you create user accounts and bind permissions. When you access the dashboard, a login window will appear. Click on the Click here to generate link:
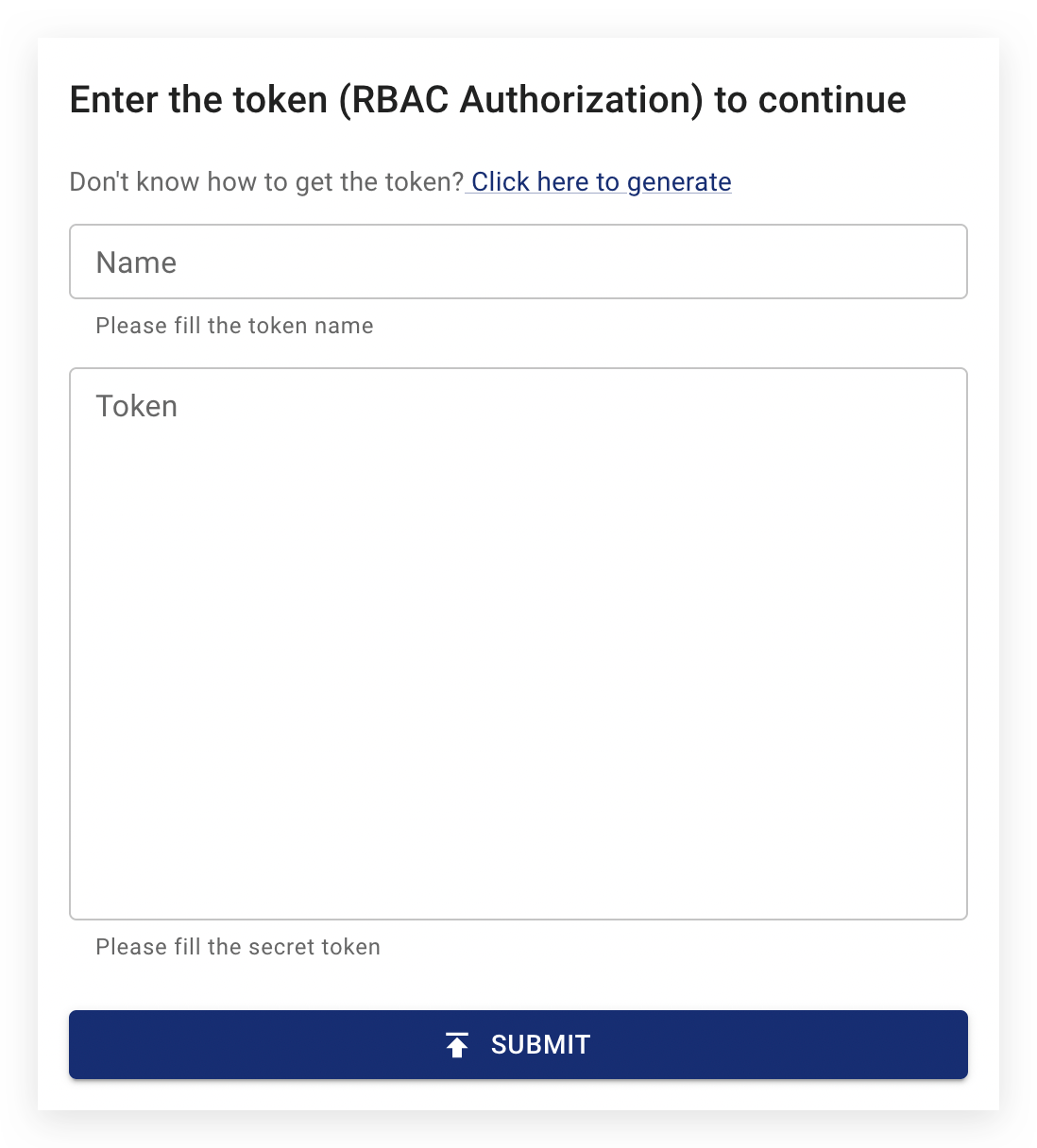
When you click on the link, a Token Generator will appear, as follows:
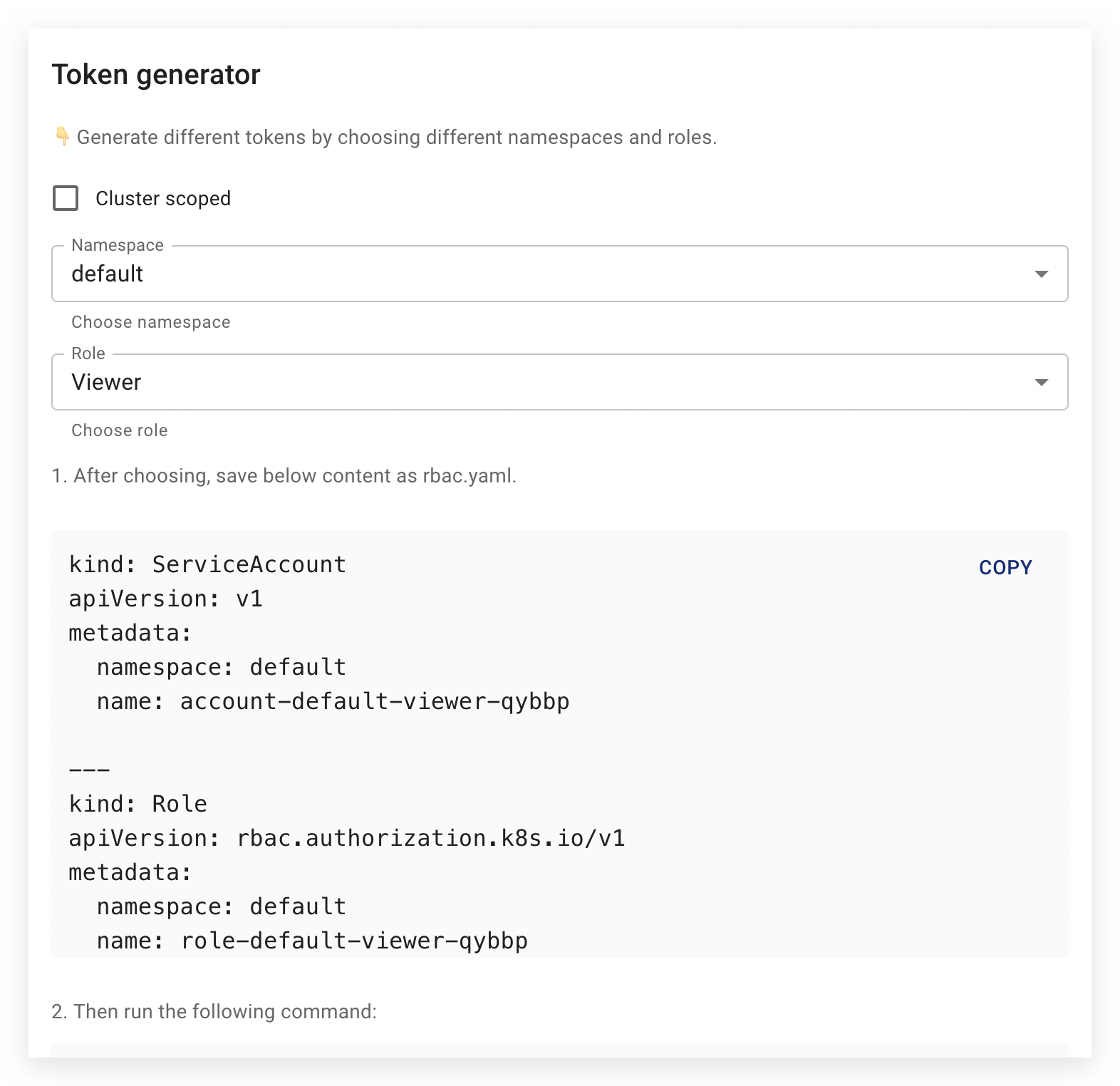
The steps to create user accounts and bind permissions are as follows:
Choose the scope of permissions
If you want to give the account the appropriate permissions for all chaos experiments in the cluster, tick the Cluster scoped checkbox. If you specify a namespace in the Namespace dropdown, the account will only have permissions in the specified namespace.
In summary, there are two options to choose from:
Cluster scoped: the account has permissions for all chaos experiments in cluster.Namespace scoped: the account has permissions for all chaos experiments in the specified namespace.
Select the role of users
Currently, Chaos Mesh provides the following user roles
Manager: who has all permissions to create, view, update and delete chaos experiments.Viewer: who only has the right to view chaos experiments.
Generate the permission
Once the permission scope and user role have been defined, the Dashboard will display the corresponding RBAC configuration in the Token Generator. For example, the permission for a manager with the default namespace will look like this:
kind: ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: account-default-manager-vfmot
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: role-default-manager-vfmot
rules:
- apiGroups: ['']
resources: ['pods', 'namespaces']
verbs: ['get', 'watch', 'list']
- apiGroups:
- chaos-mesh.org
resources: ['*']
verbs: ['get', 'list', 'watch', 'create', 'delete', 'patch', 'update']
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: bind-default-manager-vfmot
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: account-default-manager-vfmot
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: role-default-manager-vfmot
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Click COPY in the top right corner of the configuration section to copy the RBAC configuration and then save the contents locally as rbac.yaml.
Create the user account and bind permissions
Run the following command in your terminal:
kubectl apply -f rbac.yaml
You need to ensure that the local user running kubectl has permissions to the cluster so that they can create user accounts, bind permissions for other users and generate tokens.
Get the token
Versions of Kubernetes before v1.22 automatically created long term credentials for accessing the Kubernetes API. In recent versions of Kubernetes, you must manually create a service account token Secret.
For more details, see Manually create an API token for a ServiceAccount.
Copy the command shown in the third step to the Token Generator and run it in your terminal. The following is a sample command:
kubectl describe -n default secrets account-default-manager-vfmot
The output is as follows:
Name: account-default-manager-vfmot-token-n4tg8
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: account-default-manager-vfmot
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: b71b3bf4-cd5e-4efb-8bf6-ff9a55fd7e07
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1111 bytes
namespace: 7 bytes
token: eyJhbG...
Copy the token at the bottom and use it in the next step to login.
Log in to Chaos Dashboard with the user account you have created
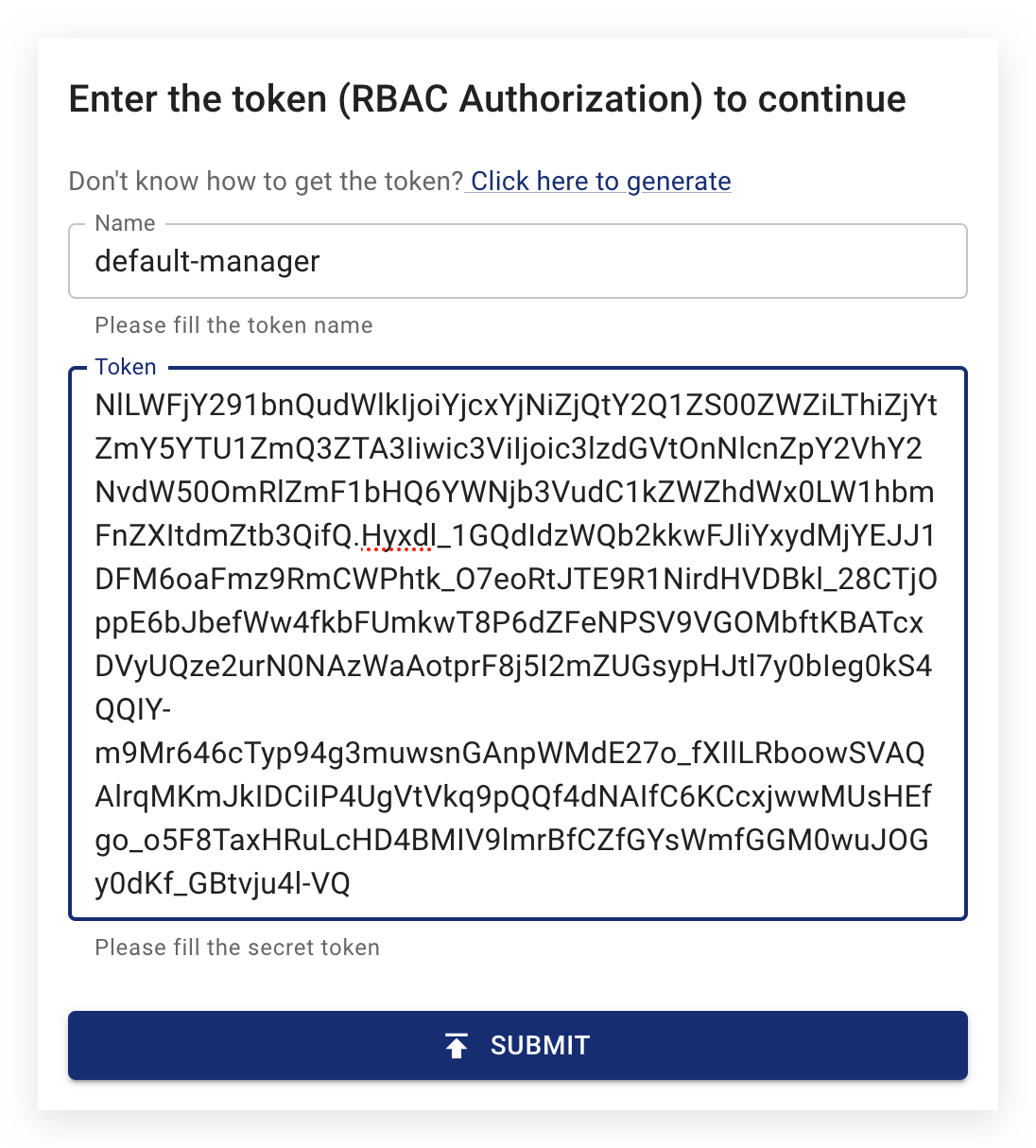
Close the Token Generator. In the Token field, enter the token you obtained in the previous step and in the Name field, enter a meaningful name for the token. It is recommended that you use a name that is a combination of the permission scope and the user role, e.g. default-manager. Once you have completed these two fields, click Submit to log in:
If you have not deployed Chaos Dashboard, you can also generate RBAC configurations by yourself and then use kubectl to create user accounts and bind permissions.
Log out of Chaos Dashboard
If you need to replace the token with another one, click the Settings on the left side bar of the Dashboard:
At the top of the page you will see the Logout button. Click it to log out the current account.
FAQ
Enable or disable permission authentication
When Chaos Mesh is installed using Helm, Permission Authentication is enabled by default. For production environments and other high security scenarios, it is recommended to leave permission authentication enabled. If you are just trying out Chaos Mesh and want to quickly create chaos experiments, you can set --set dashboard.securityMode=false in a Helm command to disable authentication. The command looks like this:
If you want to enable the permission authentication again, then reset --set dashboard.securityMode=true in a Helm command.